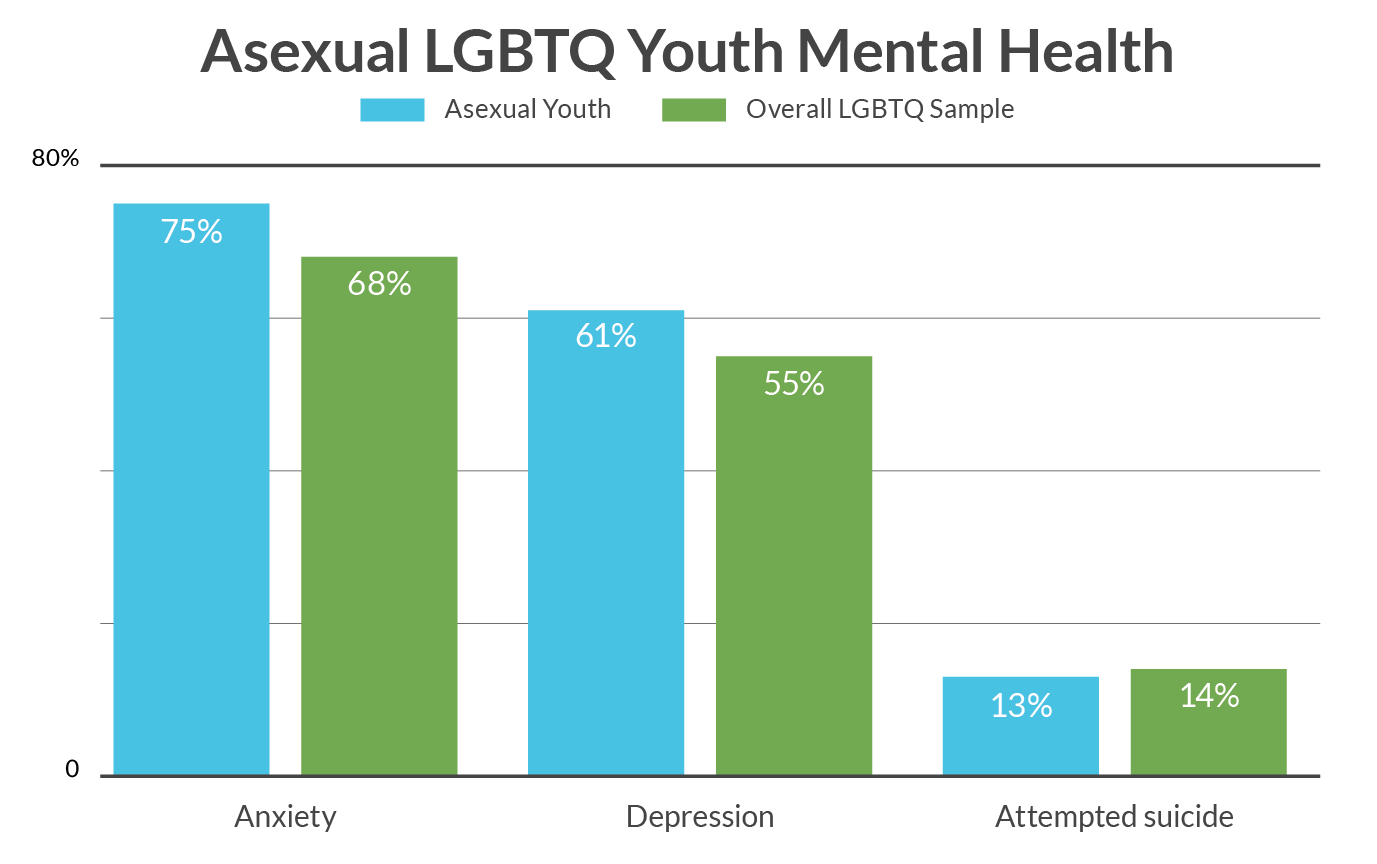
Introduction to Asexual Identity and Its Significance Asexual identity, characterized by the lack of sexual attraction towards others, is an important aspect of human diversity. While sexual orientation and gender identity have gained significant attention and acceptance in recent years, asexual individuals continue to face significant challenges, particularly teenagers in Asia. This article aims to shed light on the rising trend of asexual hate crimes targeting teenagers in Asia and the need for increased awareness and support for this marginalized community. Understanding the Root Causes of ‘A’ Phobia Asexual adolescents sometimes face discriminatory or dismissive attitudes or behaviors both within and beyond the LGBTQ+ community. Disbelieving attitudes towards asexuality can leave asexual teenagers afraid to come out. Behaviors and attitudes that are considered discriminatory include the idea that asexuality is a mental illness, that asexuality is a phase or a choice, the idea that asexual people cannot feel love, and those that make asexual people feel dehumanized. To comprehend the underlying causes of asexual hate crimes targeting teenagers in Asia, it is crucial to examine the prevailing societal norms and cultural expectations. In many Asian societies, there is a strong emphasis on traditional gender roles and expectations of marriage and procreation. Asexual individuals, who do not conform to these norms, are often shamed and considered abnormal. This stigmatization arises from a lack of understanding and awareness about asexuality, perpetuating harmful stereotypes and discrimination. Higher Rates of Depression and Anxiety There has been a lack of research on asexuality, despite growing calls from within the asexual community for increased visibility and awareness. Even less is known about asexual youth. Using data from The Trevor Project’s 2020 National Survey on LGBTQ Youth Mental Health, this brief explores sexual orientation, gender identity, and mental health indicators among asexual youth. In our sample of over 40,000 LGBTQ youth, 10% identified as asexual or ace spectrum. When given additional options to describe their sexual orientation, asexual youth further selected demi sexual (15%), polyamorous (9%), and greysexual (9%). And consistent with previous research, many asexual youth also selected romantic attraction labels such as pan romantic (20%), biromantic (17%), and aromantic (13%). Asexual youth reported higher rates of depression and anxiety compared to the overall LGBTQ sample. Asexual LGBTQ youth reported slightly greater rates of symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (aOR = 1.12, p<.001) and major depressive disorder (aOR = 1.19, p<.001) in the past two weeks compared to LGBTQ youth who did not identify as asexual. Rates of attempted suicide in the past year were slightly lower for asexual youth (aOR = .82, p<.001). A larger proportion of asexual youth were transgender or nonbinary compared to the overall sample of LGBTQ youth. Overall, 25% of the LGBTQ youth in our sample were transgender or nonbinary, and 9% were questioning if they were. This compares to 41% of asexual youth who were transgender or nonbinary, and 13% who were questioning if they were transgender or nonbinary. Within these broader categories, 3% of cisgender men, 9% of cisgender women, 6% of transgender women, 13% of transgender men, 20% of nonbinary youth, and 15% of youth who were questioning their gender identified as asexual. The Impact of Shaming Teenagers for Not Having Sexual Attraction Shaming teenagers for not having sexual attraction can have severe consequences on their mental health and overall well-being. Adolescence is a critical period of self-discovery and identity formation, and teenagers who identify as asexual may already grapple with feelings of confusion and isolation. The added burden of societal shaming further exacerbates their struggles, leading to increased rates of depression, anxiety, and even suicide attempts among asexual teenagers in Asia. The Rising Trend of ‘A’ Phobia Targeting Teenagers in Asia In recent years, Asia has witnessed an alarming surge in ‘A’ Phobia & hate crimes targeting asexual teenagers. These hate crimes manifest in various forms, such as verbal abuse, physical assaults, and online harassment. Asexual teenagers often find themselves ostracized, stigmatized, and marginalized due to their lack of sexual attraction. This discrimination not only affects their mental and emotional well-being but also poses serious threats to their physical safety. Forced Marriage and the Violation of Asexual Rights One of the distressing outcomes of societal pressure is the prevalence of forced marriages among asexual teen age girls in South Asia. Asexual individuals often face immense familial and societal pressures to conform to societal expectations of marriage and procreation. Forced marriages not only violate their autonomy and agency but also subject them to a lifetime of emotional and physical trauma. Such marriages often lack the necessary consent and understanding, further exacerbating the marginalization experienced by asexual individuals. Intimate Partner Rape and the Lack of Consent in Allow-Ace Relationships Within asexual relationships, the lack of sexual attraction can create a power dynamic that leaves asexual individuals vulnerable to sexual coercion and intimate partner/spousal rape. Asexual individuals may find it challenging to establish boundaries and communicate their lack of desire for sexual intimacy, leading to violations of their bodily autonomy. The lack of understanding and awareness about asexual relationships contributes to the normalization of non-consensual sexual acts within these unions, perpetuating harm and further marginalizing asexual individuals. Breakup Rates among Asexual Individuals and Its Consequences for Asexual Individuals The pressure to conform to societal expectations of allo-ace relationships takes a toll on asexual individuals, often resulting in high divorce/breakup rates. Asexual individuals who enter into marriages under societal pressure may struggle to maintain relationships that lack the fundamental element of sexual attraction. The strain caused by this disconnect can lead to emotional and psychological distress, ultimately culminating in the dissolution of marriages. The stigma and judgment associated with divorce further contribute to the marginalization of asexual individuals within society. Addressing the Low Awareness and Limited Support for Asexual Individuals One of the key issues faced by asexual teenagers in Asia is the lack of awareness and support within their communities. Educational institutions, healthcare providers, and policymakers must prioritize the inclusion of asexual experiences in their curricula, training, and policies. By